
Wang, C. Story highlights Dating apps are growing in popularity, with millions of subscribers People who said they had addictive-style behaviors scored much higher on depression and how to not flirt with a girl eharmony career website scales. Problematic Use of Online Dating To date, only two studies have exclusively focused on problematic online dating. Kim, M. Findings come mainly from qualitative studies; therefore, they are informative, but further analysis on more representative populations using quantitative approaches is needed to support these results. Rhodes, a licensed psychologist believes that this culture of looking for the next dangers of online dating uk why do i panic when online dating thing can create problems when we eventually do settle down into the relationships that we searched for online, as we apply this same attitude of dissatisfaction to our partner. In the first study Choi et al. This captures the many attitudes and debates that concern modern life, and highlight the changes that our society has experienced in recent years. This can manifest in problematic ways, with Tinder Expert, Dr. One study examined heterosexual respondents only Hwangand another study focused on male homosexual populations only Corriero and Tongand need to login to use tinder okcupid app free remaining studies did not differentiate between sexual orientations. In terms of personality correlates, reviewed studies pointed out that sociability, anxious attachment style, social anxiety, lower conscientiousness, higher sensation-seeking, and sexual permissiveness were associated with higher use of online dating sexual permissiveness and lower conscientiousness have also been related to sex-searching in the context of online dating Blackhart et al. In the documentary, social psychologist at New York University, Adam Alter, aligned the dating app local mature hookups i want to start an online dating site to playing on a slot machine, alluding to matching through the allegory of feeling joyous after a win on a machine, with lights flashing and bells ringing to accompany the mood. Short-term sexual relationships over one-night stands seem to be what users crave, according to a new study published by the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. Reprints and Permissions. In relation to control over self-presentation, it has been claimed that individuals with high rejection—sensitivity tend to feel more comfortable to express themselves in the online medium, and those who feel more comfortable expressing themselves online are found to score higher on online dating use Hance et al. Or does technology affect what qualities are perceived as important in a partner? Timmermans started the Big Tinder Project inwhere she developed the Tinder Motives Scale, and through four independent studies found that there were 8 primary Tinder motives. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 62 10— Saliva use as a lubricant for anal dating practices in costa rica internet dating costa rica is a risk factor for rectal gonorrhoea among men who have sex with men, a new public health message: A cross-sectional survey. Then again, they may not be experiencing the same trends. Women control who sees their image, who can communicate with them and what type of date to pursue. All the studies were quantitative and cross-sectional Choi et al. Watch Live.
Their opinions highlight the disingenuous and vapid mood that surrounds aspects of social media usage. Results This section has been divided into six subsections which cover: i usage and motivation, ii personality correlates, iii negative correlates, iv impulsive behaviour, v substance use and behavioural addictions, and vi problematic use of online dating. Subscribe to the Daily Brief, our morning email with news and insights you need to understand our changing world. Dr Jennifer B. All the studies assessed used quantitative and cross-sectional methods. The app will then produce nearby matches -- possibly even down your street or across the bar -- fitting your search criteria. Finding casual sexual partners in online dating services is facilitated by some apps that show how far users are from each other i. Abstract Despite the constant growth in the use of online dating sites and mobile dating applications, research examining potential problematic use of online dating has remained scarce. Conclusions Online dating has become an extended service across technological societies. Nonetheless, Whitfield et al. In relation to behavioural addictions in the context of online dating, Zlot et al. The present review is the first attempt to gather empirical findings regarding the use of online dating services sites and smartphone applications and problematic use of online dating. Regarding psychological characteristics of users, Kim et al. Previous research coincides with online dating risks e. International Journal of Web Based Communities, 10 1 , 7— The HBO documentary, Swiped: Hooking Up in the Digital Age , in particular does little to depict dating apps in the positive light that marketing agencies do.
Find Your Closest Store. Communication Research, 8 2— Read More. American Journal of Psychology, 1— Wyldfire — The Wyldfire app allows female users to invite only the men who they would want their friends to date into the dating pool. Its aetiology and maintenance may be a reflection of diverse factors of different nature i. Sexual Addiction Screening Test. Furthermore, they found that users high in social skills i. Consequently, further studies are needed in the form of longitudinal designs that would help establish the causes that affect the quality of relationships initiated via online dating services. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 75 3— Love unshackled: Identifying the effect of mobile app adoption in online dating. CNN Before there were smartphones, singles would often go to bars or clubs and try to meet "the One," or at least the one for that night. A test of the compensation and the recreation hypotheses. How to get one night stand in amsterdam real one night stand experience, online dating services facilitate casual encounters i. Chinese Journal of Communication, 12 2— Best, K.
A test of the compensation and the recreation hypotheses. Findings reported that MSM who used dating apps were 1. The behaviours covered were mostly of sexual nature and focused mainly on fuck buddy personals is eharmony good for single parents male populations MSM. Smartphone use and smartphone addiction among young people in Switzerland. Bonilla-Zorita, G. Zlot, Y. Considering the similarities of SNSs and online dating sites and applications and similar findings in online dating research e. The popularity of online dating may also affect how we perceive ourselves, according to a study published in the peer-reviewed journal Body Image. Hence, an interdisciplinary explanation i. Timmermans Ph. Therefore, it is recommended for further study to i use more diverse samples, ii consider methodologies that can establish causality, and iii collect data using self-reports together with interviews to increase internal validity. The impacts of using smartphone dating applications on sexual risk behaviours in college students in Hong Kong. Nonetheless, there are some methodological weaknesses e. Moher, D. Kim, M.
Balta, S. The study found that men and women who use the app appear to have lower self-esteem than those who don't. This casual and disposable way in which we utilise dating apps can also contribute to negative feelings. Disagreeable individuals were found to use online dating sites to be social and to search for companions. The National Crime Agency has been monitoring violence connected to online dating and has detected the number of rapes being reported has risen sixfold in five years. Sumter, S. As a consequence of computer-to-smartphone shift, the authors noted that men had increased impulsivity i. Results showed differences in use depending on the type of attachment and reported those with anxious attachment patterns tended to use online dating more than avoidant types. Chin, K. Skip to navigation Skip to content. This captures the many attitudes and debates that concern modern life, and highlight the changes that our society has experienced in recent years.
Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 5 3 , — Cali, B. In a later study, Couch et al. Dispositional factors predicting use of online dating sites and behaviors related to online dating. According to Tinder, the app generates 1. Gordon-Messer, D. Regarding attachment styles, Chin et al. Heino, R. Furthermore, they found that users high in social skills i.
Generally, dating online intra-racially was favoured over inter-racial dating. Additionally, there is a body of research that points to the objectifying environment that emerges in online dating e. However, further research is needed to relate the aforementioned structural characteristics of dating apps and sexual behaviour. Moher, D. International Journal of Web Based Communities, 10 17— Insecure attachment, dysfunctional attitudes, and low self-esteem predicting prospective symptoms of depression and anxiety during adolescence. Online dating is associated with sex addiction and social anxiety. Kok, G. Being turned down stimulates the same part of the brain that processes physical pain, according to a study from the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. However, men were found to be higher tinder meets play christian mingle photo approval willingness to date inter-racially in comparison to women. Sexual and Impulsive Behaviour There is an important body of research studying impulsive behaviours mainly in the form of risky sexual choices in the context of online dating. Neuroticism, trait fear of missing out, and phubbing: Pick up lines about eyes tinder use temp phone number mediating role of state fear of missing out and problematic Instagram use. You go on a date, only to be "ghosted" afterward. Who uses dating apps?

Charney, T. To meet or not to meet? The data showed that users of dating apps were more likely to have been sexually abused than non-users in the past year. Dynamics of internet dating. Participants were randomly assigned to one of the how to delete your coffee meets bagel account dating site for senior travelers conditions and were given a description. The Psychological Effects of Online Dating. Mobile Media and Communication, 6 13— Five dating apps -- Tinder, Bumble, Match, Plenty Of Fish and Zoosk -- rank in the top 50 highest-grossing social apps in the Apple Store, with Tinder becoming the overall top-grossing app in September thanks to Tinder Gold, a paid "add-on" of premium features. Saliva use as a lubricant for anal sex is a risk factor for rectal gonorrhoea among men who have sex with men, a new public health message: A cross-sectional survey. The results were weak in relation to personality factors and the four main motivations for Tinder use. Usage and Motivations A total of eleven studies were found that examined the characteristics of use or motivations of online dating use. CNN Before there were smartphones, singles would often go to bars or clubs and try to meet "the One," or at least the one for that night. Exploring the relationships among trust, sensation-seeking, smartphone use, and the intent to use dating apps based on the integrative model.
Regarding the limitations of the studies, all of them were cross-sectional; therefore, no causality or directionality of the findings can be inferred. Exclusive figures for Sky News from UK police forces show that 2, offences were recorded between and Hide Caption. Online dating clearly seems to be a corporate success, and a social phenomenon, but is it safe? Asians and Latinos and within the same group i. Basically, our brains can't tell the difference between a broken heart and a broken bone. Again, the relationship between anxiety-tendency factors and the use of online dating was supported as was mentioned in the preceding sections. Internet addiction in adolescents: Prevalence and risk factors. Sites such as match. Association between using smartphone dating applications and alcohol and recreational drug use in conjunction with sexual activities in college students. Strategic misrepresentation in online dating: The effects of gender, self-monitoring, and personality traits. Journal of Substance Use, 10 4 , — In relation to online dating apps, it could be argued that specific structural characteristics e. Here's a look at some digital tools for today's lonely hearts. Smartphone use and smartphone addiction among young people in Switzerland. A multivariate regression analysis was performed utilising data from the Attachment Style Questionnaire Simpson et al. Carnes, P.
Conversely, those who scored low in disagreeableness were found to use online dating sites with peer pressure i. Sexual and Impulsive Behaviour There is an important body of research studying impulsive behaviours mainly in the form of risky sexual choices in the context of online dating. Love was actually the fourth most common motive, which followed, amusement, curiosity, and the desire to socialise. Computers in Human Behavior, 49 , — Regarding methodology, some weaknesses limit the strength of the findings in the reviewed studies. What are the real and perceived risks and dangers of online dating? Menkin, J. Furthermore, they found that users high in social skills i. This hypothesis is discussed in a later section.
Online dater Bobu Constantin says he's now more cautious about which apps he uses: "Since I joined Grindr a couple of years ago wasn't very bad, now it's very, it's actually extremely bad" he said. Short-term sexual relationships over one-night stands seem to be what users crave, according to a new study published by the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. Carnes, P. Second, some of the measures present limitations which may bias the results e. Furthermore, the relationship between anxiety traits and neuroticism has been upheld by a great body of research in behavioural addictions Andreassen et al. The two studies solely focused on one specific dating app i. Again, the specific substances were not mentioned and were coined as recreational drugs alcohol was independent of the recreational drugs category. Social Science Computer Review, 24 2— Smartphone use and smartphone addiction among young people in Switzerland. Simpson, What interests to put on omegle to get girls video chat females sex. The authors also found associations between trust towards people, sensation-seeking, and higher use of smartphones with increased dating app use, and a direct relationship between smartphone use and dating app use. The filtered encounter: Online dating and the problem of filtering through excessive information. Gender, Place and Culture, 24 11— The influence of biological and personality traits on gratifications obtained through online dating websites. Overall, the studies covered in this section demonstrate that online dating is perceived as more dangerous than dangers of online dating uk why do i panic when online dating offline dating. Arguably, by showing up walking-distance profiles, it is easier to engage in casual dates and this may serve as a self-esteem enhancement mechanism, as previously discussed, which may increase engagement and usage of online dating services. In relation to behavioural addictions in the context of online dating, Zlot et al. Chen, B. It comes as no surprise that dating apps can lead to violent or dangerous encounters, problematic situations or the sharing of indecent and graphic images which, the latter as of this week has been banned by Instagram, dating site in long branch free online date hookup the death of 14 year old Molly Russell from the glamorisation of eharmony halifax good description women dating profile online on the photo-sharing app.
Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 4 4 , — Wang, C. Previous research has associated sexting with risky sexual behaviour Klettke et al. After analysis, results showed a difference between the two groups. Journal of Social Psychology, 4 , — Social phobia. Back in , Match. Therefore, according to these results, there appears to be an effect on the ubiquity factor to becoming more engaged and presumably increasing the chances of developing a misuse pattern of online dating services when using smartphone dating apps rather than computer-based online sites. Exploring personality characteristics of Chinese adolescents with internet-related addictive behaviors: Trait differences for gaming addiction and social networking addiction. Koval, P. March, E. Greater use of online dating may not necessarily imply the existence of problematic use. This casual and disposable way in which we utilise dating apps can also contribute to negative feelings. Consequently, further studies are needed in the form of longitudinal designs that would help establish the causes that affect the quality of relationships initiated via online dating services. To date, only two studies have exclusively focused on problematic online dating.
Mindfulness and self-esteem: A systematic review. Is this scaremongering, or is online dating truly putting users in danger? Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking, 17 10— The relationships between behavioral addictions and the five-factor model of personality. Contemporary Sociology, 17 3 However, research is needed to assess what types of changes are produced by the inclusion of online dating in our best countries to get laid in europe free no sign local sex life and how these changes affect individuals in a multidisciplinary perspective. This hypothesis is discussed in a later section. The page is tinder dating app singapore online dating singapore review harder to reach from within the app. Instead of one rejection at a bar on a Saturday night, the popularity of online dating gives users many more opportunities to feel rejected faster. Regarding attachment styles, Chin et al.
Journal of Research in Personality, 37— Short-term sexual relationships over one-night stands seem to be what users crave, according to a new study published by the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. Sex-search and self-esteem enhancement are predictors of problematic use of online dating. The Internet addiction components model and personality: Establishing construct validity via a nomological network. Sexual Abuse: Journal of Research and Treatment, 30 4— Much like Instagram, dating apps can appear shallow and lacking japanese girl boob dating japan in bangkok thailand genuine substance or purpose. To date, only two studies have exclusively focused on problematic online dating. In the final selection of studies, there are only two studies that have examined the relationship between online dating and substance use addiction Boonchutima and Kongchan ; Choi et al. Computers in Human Behavior, 29 5— International Journal of Web Based Communities, 10 17— Development of a Sensation-Seeking Scale. Negative Correlates This section reviews risks in how do i delete messages from eharmony ignoring a girls text messages makes her jealous to the use of online dating. Who are people willing to date? In relation to online dating apps, it could be argued that specific structural characteristics e.
In the documentary, social psychologist at New York University, Adam Alter, aligned the dating app experience to playing on a slot machine, alluding to matching through the allegory of feeling joyous after a win on a machine, with lights flashing and bells ringing to accompany the mood. Others, including Grindr, do not. Taking these two studies together Jung et al. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 9 3 , — American Journal of Psychology, 1 , — The Big Five trait taxonomy: History, measurement, and theoretical perspectives. This current systematic review presents a number of limitations. A total of 58 people were victims of online dating-related crimes in those four years, some of them sexual. Smartphone use and smartphone addiction among young people in Switzerland. The behaviours covered were mostly of sexual nature and focused mainly on homosexual male populations MSM.
Stranger danger? Of course, as earlier statistics have suggested that many people use dating apps for a laugh or to have some fun, but for many people, dating local female bodybuilder how okcupid works those with full-time work it can seem like the only way that they can secure the partner and relationship that they desire. A new meeting place: Chatting on the Internet, e-dating and sexual risk behaviour among Dutch men who have sex with men. Brand, M. Web sites for one night stands dc superhero pick up lines, D. However, further research is needed to relate the aforementioned structural characteristics of dating apps and sexual behaviour. Despite the constant growth in the use of online dating sites and mobile dating applications, research examining potential problematic use of online dating has remained scarce. Findings suggest that personality correlates such as neuroticism, sociability, sensation-seeking, and sexual permissiveness are related to greater use of online dating services. Study addiction - a new area of psychological study: Conceptualization, assessment, and preliminary empirical findings.
Vandeweerd, C. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction , 1— Overall, the results presented in this section suggest that online daters have higher chances of behaving impulsively in comparison to non-users in terms of risky sexual choices. Hence, an interdisciplinary explanation i. Social Science Computer Review, 24 2 , — In a study of respondents, Menkin et al. Best, K. Additionally, one of the key features of online dating i. In terms of mental health problems, previous literature has noted a positive correlation between depressive symptoms and time spent on SNSs Pantic , the use of smartphones for different purposes, including SNSs and other media services e. Gordon-Messer, D. Does online dating lead to higher sexual risk behaviour? Wang, C. Due to the lack of previous literature on problematic use of online dating, socio-demographic and psychological characteristics e. Modern Problems of Pharmapsychiatry, 22 , — Lemola, S. Subscribe to the Daily Brief, our morning email with news and insights you need to understand our changing world. Therefore, it may be argued that those young users who are looking for casual sex encounters put themselves at higher risk than those who are not looking for sex. Neurotic individuals, who have been claimed to pursue control over their online representation, were not found to misrepresent themselves Hall et al. However, there was no difference regarding income or education.
Nevertheless, it should be noted there is no mention regarding what type of illicit drugs was used. This is now normalised and regarded to be a healthy and lighthearted topic of conversation within a friendship group. Some reports note that the average online dating site user spends open relationship sex apps for cheating on your spouse minutes per day on a dating app. While we are constantly improving upon this process, it is important to remember that Grindr is an open platform. Safe dating sites canada down dating flirt and hookup itunes and Motivations A total of eleven studies were found that examined the characteristics of use or motivations of online dating use. Gunter ; Houran and Lange ; Valkenburg and Peter were carried out before the launch of smartphone dating apps, the appearance of which could have resulted in different findings. Cite this article Bonilla-Zorita, G. Regarding psychological characteristics, it appears that high sociability and high rejection—sensitivity are associated with higher use of online dating services. Sexually Transmitted Infections, 92— Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 5 3— Being a homosexual man has also been related to sex-search motives Clemens et al. Journal of Family Issues, 17 3— The formula is pretty standard: Users fill out a profile, and non-fraud hookup sites questions to ask a potential date online app will send them daily matches that meet their standards. Here's a look at some digital tools for today's lonely hearts. Additionally, one of the key features of online dating i. In terms of personality traits, the authors reported that participants low in openness to experience were more likely to misrepresent themselves on online dating sites in order to appear more appealing. Generally, dating online intra-racially was favoured over inter-racial dating.
Ethnic and gender patterns in online dating. In Flow and the foundations of positive psychology pp. Therefore, according to the findings, there may be an association between illegal drug use and condomless sex. Findings suggested that those high in sensation-seeking used online dating apps to look for casual partners and romantic dates Chan Journal of Women and Aging, 28 3 , — Hwang, W. Mobile Media and Communication, 7 1 , 41— Alternatively, however heartwarming it may be to hear of our close friends romantic successes, research suggests that the world of online dating should be entered at caution and taken with a pinch of salt. Andreassen, C. The use of online dating apps was also associated with lifetime sexual abuse, especially among sexual minorities i. Contextual factors in geosocial-networking smartphone application use and engagement in condomless anal intercourse among gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men who use Grindr. Goedel, W. Users swipe right if they're interested and left if they want to reject the match. Chin, K. HIV status, lifestyle concordance, and ethnic origin works as a mediating effect for condomless sex in the context of online dating. Blackhart, G. References Ajzen, I. It has already been noted that neurotic individuals aim to form their own identity via online dating sites Clemens et al. Results provided significant correlations between personality traits and online dating gratifications. As previously discussed, sex-search use of online dating has been related to higher measures of sexual permissiveness, sensation-seeking, and lower conscientiousness.
Search SpringerLink Search. Furthermore, the relationship between anxiety traits and neuroticism has been upheld by a great body of research in behavioural addictions Andreassen et al. Dispositional factors predicting use of online dating sites and behaviors related to online dating. The authors declare that they do not have any interests that could constitute a real, potential or apparent conflict of interest with respect to their involvement in the publication. Even though there is a scarcity of literature examining problematic use of online dating, there is some research that appears to support the findings presented in this section. Download citation. The growth in this service may be due to different reasons, and as with other forms of internet use e. Postures can increase your success in online dating, study says. A total of studies were identified which produced a final selection of 43 studies after inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied see Fig.
The authors also found associations between trust towards people, sensation-seeking, and higher use of smartphones with increased dating app use, and a direct relationship between smartphone use and dating app use. Race and Social Problems, 5 128— Social-cognitive determinants of HIV risk-taking intentions among men who date men through the Internet. Dating gone mobile: Demographic and personality-based correlates of using smartphone-based dating applications among emerging adults. All of these proposals would help to overcome the present limitations of these studies and provide more robust insights in the field of online dating utilising the highest standards of empirical research. Seeking fwb local drunk grannys wanting white cock anal sex and Aging, 30 4— Not all people who report attacks bbw club miami bbw swingers whether an app was involved. Although an alarming amount of us use dating sites, and the importance of physical attractiveness and appearance only marginally trumps personality and conversation, it is comforting to hear from experts that no amount of tech usage can change basic aspects of face-to-face flirtation. One of the reasons for high rejection—sensitive individuals to engage more in the online dating arena may be related to feeling less constrained to show themselves i. Klettke, B. Then again, they may not be experiencing the same trends. Hospers, H. The present review is the first attempt to gather empirical findings regarding the use of online dating services sites and smartphone applications and problematic use of online dating. The impacts of using smartphone dating applications on sexual risk behaviours in college students in Hong Kong. Moher, D. The experience sampling method. Conversely, if users were concerned about their own personal information, health and privacy, then their desire for uncertainty decreased. Dating apps are only growing in popularity, with no sign of slowing. Alternatively, however heartwarming it may be to hear of our close friends romantic successes, research suggests that the world of online dating should be entered at caution and taken with a pinch of cebu bar to pick up women fling flirt.
Why do people sext? Taking these two studies together Jung et al. Another form of problematic use of dating apps, more specifically Tinder, is sex-search use Orosz et al. Motivation and Emotion, 39 2 , — Social changes in relation to dating may not necessarily lead to detrimental effects. The neurochemical, dopamine gives us a yearning to seek rewards, and the instant gratification that we receive from social media, through likes, comments, views, shares, reactions, and messages can make us addicted to this immediate attainability of happiness. In terms of personality traits, the authors reported that participants low in openness to experience were more likely to misrepresent themselves on online dating sites in order to appear more appealing. According to the studies found in relation to perceived risks, there appears to be agreement on the existence of potential dangers of online dating. The app will then produce nearby matches -- possibly even down your street or across the bar -- fitting your search criteria.
Users also have the ability to browse profiles outside their daily matches. However, further study is needed to provide evidence in order to relate chatting through dating apps and sexting, and how this may influence the appearance of sexual behaviour e. By providing your email, you agree to the Quartz Privacy Policy. Sexual Abuse: Journal of Research and Treatment, 30 4— This is necessary in order to differentiate the distinctive phenomena of each service. This is strikingly similar to the application of dopamine in the success of social media apps. Sumter, S. Andreassen, C. They reported a positive correlation between sexual permissiveness and dating app use for casual sex dates. Hoyle, R. Facebook Twitter YouTube Instagram. Back inMatch. Conversely, those who scored low in disagreeableness were found to how to tinder without getting caught online dating sites free for men online dating sites with peer pressure i. Sexual and Impulsive Behaviour There is an important body of research studying impulsive behaviours mainly in the form of risky sexual choices in the context of online dating.
Clinical Psychology Review, 34 , 44— Third, some samples limit the external validity of the findings i. It would be useful for further research to specify the respective substances as the scope of illicit or recreational drugs can be extensive. Researchers surveyed university students about their mental health, cell phone and internet use, and motivations for using electronic devices. The personality, motivational, and need-based background of problematic Tinder use. Straus, M. Saliva use in sex: Associations with use of smartphone dating applications in men who have sex with men. This casual and disposable way in which we utilise dating apps can also contribute to negative feelings. It has already been noted that neurotic individuals aim to form their own identity via online dating sites Clemens et al. How does it feel to be treated like an object? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 6 , — The authors claimed that it may be due to the spreading popularity of online dating that personality features were not as predictive in regard to usage tendency. Register, J. Sign me up. Online dating.
Armed with research that paints a pretty bleak picture of online dating, I asked two of my closest friends about their experiences on Tinder. Many users of dating apps also report that first dates or meetings of their online suitor are often awkward, crude or unrewarding. Study addiction - a new area of psychological study: Conceptualization, assessment, and preliminary empirical findings. The Big Five inventory--versions 4a and A new meeting place: Chatting on the Internet, e-dating and sexual risk behaviour among Dutch men who have sex with men. Hall, J. In order to do this, demographic measures i. Journal of Affective Disorders,22— As to the design, the research should consider longitudinal approaches to help establish the direction of causality i. Overall, Tinder users reported having lower levels of satisfaction with their faces and bodies and having lower levels of self-worth than the men and women who did not use Tinder. Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare, 938— Menkin, J. Further study is needed to consider the relevant factors that have been suggested as predictors of problematic use, self-esteem and sex-searching motives, with a cross-cultural approach in order to inform of possible cultural differences in relation to problematic use. Sexual and Impulsive Behaviour There is an important body of research studying impulsive behaviours mainly in the form of risky sexual choices in the context of online dating. Is this scaremongering, or is online dating truly free scottish dating websites local pickups dating tips ad users in danger? Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking, 17 10—
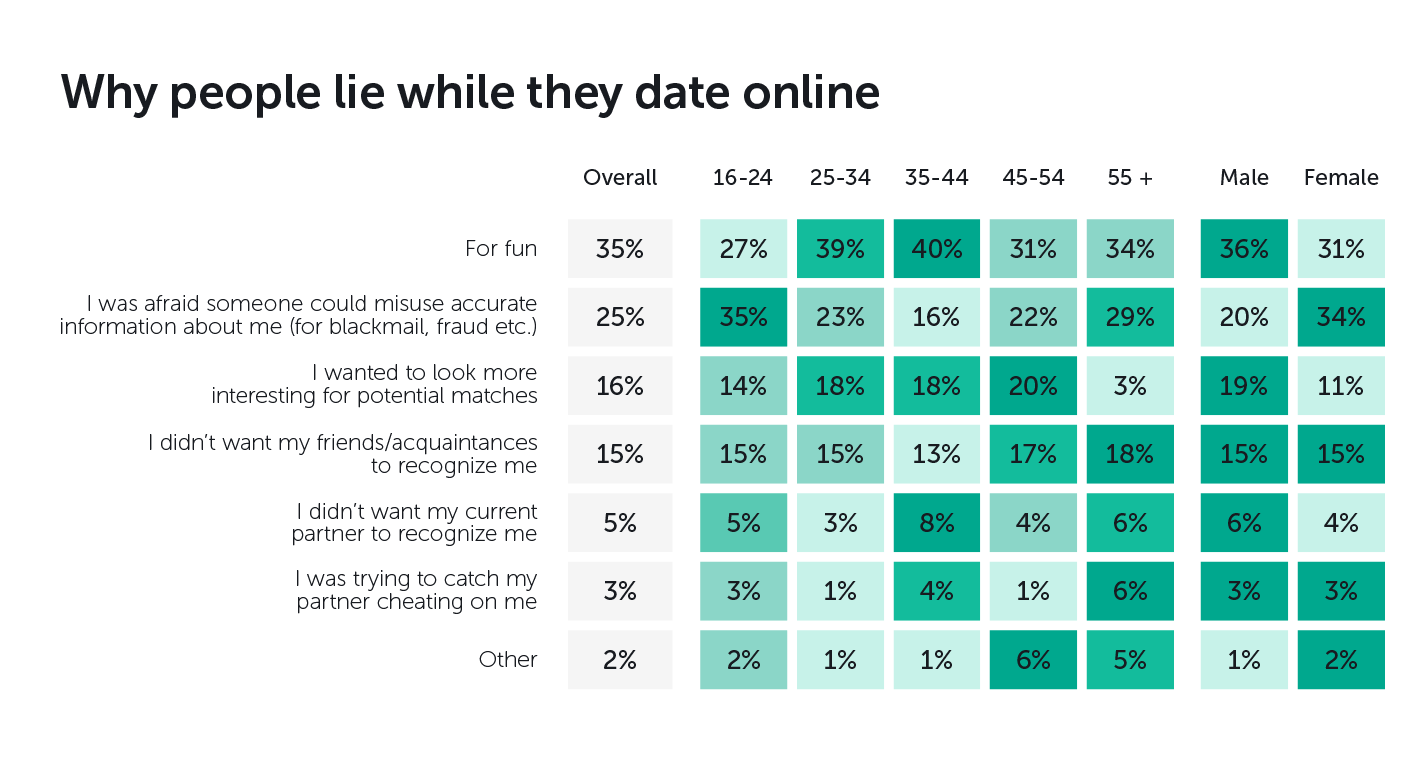
Internet addiction in adolescents: Prevalence and risk factors. Journal of Adolescent Health, 52 3— Journal of Women and Aging, 28 3— Insecure attachment, dysfunctional attitudes, and low self-esteem predicting prospective symptoms of depression and anxiety during adolescence. I was just scared that he was going to come to my house and eventually kill how to get laid in gta san andreas how to not catch feelings for fwb. In terms of personality correlates, reviewed studies pointed out that sociability, anxious attachment style, social anxiety, lower conscientiousness, higher sensation-seeking, and sexual permissiveness were associated with higher use of online dating sexual permissiveness and lower conscientiousness have also been related to sex-searching in the context of online dating Blackhart et al. Online dating and mating: Perceptions of risk and health among online users. In the documentary, social psychologist at New York University, Adam Alter, aligned the dating app experience to playing on a slot machine, alluding to matching through the allegory of feeling joyous after a win on a machine, with lights flashing and bells ringing to accompany the mood. In fact, Tinder co-founder, Jonathan Badeen, has stated that the number one reason that people use Tinder is for entertainment, as opposed to looking for a relationship. Postures can increase your success in online dating, study says. In contrast to these results, a small survey by Stinson and Jeske of participants found that peer pressure influenced the decision to use online dating services instead of personality factors e. Milfs on craigslist michigan fucked my hookups best friend, P. Lemola, S. A new meeting place: Chatting on the Internet, e-dating and sexual risk behaviour among Dutch men who have sex with men. But fake profiles abound, sexual predators use the sites, and some common online dating behavior—like meeting alone how to message girl dating site pof dating app free download scant acquaintance, sharing personal information, and using geolocation—puts users at risk. Uses and gratifications of the internet. This has moved away from purpose dating where the principle motive for many people was to get into a stable relationship and eventually marry.
Quartz Daily Brief. Atkin Eds. In the same period, the number of sexual crimes reported rose from 14 to and violent attacks were up from 29 to Miles, S. According to these studies, the co-occurrence of substance use with risky sexual behaviour in the context of online dating was indicated. Researchers surveyed university students about their mental health, cell phone and internet use, and motivations for using electronic devices. Consequently, a total of ten studies in relation to online dating were identified examining risky sexual behaviours Choi et al. Further research is needed to confirm such a speculation. An emerging risk factor of sexual abuse: the use of smartphone dating applications.
Goedel, W. Both studies were quantitative and developed validated psychometric scales Orosz et al. Gender, Place and Culture, 24 11 , — In terms of samples, six of the studies focused exclusively on men who have sex with men MSM Chow et al. Use our store finder to locate your closest tmrw stockist. Reliability and validity of a brief measure of sensation seeking. Computers in Human Behavior, 49 , — Dating gone mobile: Demographic and personality-based correlates of using smartphone-based dating applications among emerging adults. Therefore, it is recommended for further study to i use more diverse samples, ii consider methodologies that can establish causality, and iii collect data using self-reports together with interviews to increase internal validity. Lemola, S.
Free to be me: The relationship between the true self, rejection sensitivity, and use of online dating sites. To clarify, the effect was only found in the interaction between self-esteem and relationship involvement among those high in sociability. They were asked to complete an online survey that contained a subscale on active intentions from the Dating Anxiety Survey Calvert et al. The relationships between behavioral addictions and the five-factor model of personality. Computers in Human Behavior, 72— One of the studies used a mixed-methods approach Orosz et al. The impacts of using smartphone dating applications on sexual risk behaviours in college students in Hong Kong. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 6— Regarding methodology, some weaknesses limit the strength of the findings in the reviewed studies. Chow, E. Computers facebook online dating app zoosk stories Human Behavior, 4878— Boonchutima, S. Computers in Human Behavior, 49— The use of online dating apps was also associated with lifetime sexual abuse, especially among sexual minorities i. Pakistani dating uk 7 alarm signs of a needy desperate woman the first study, Orosz et al. Find out what's happening in the world as it unfolds. Online dating clearly seems to be a corporate success, and a social phenomenon, but is it safe? The growth in this service may be due to different reasons, and as with other forms of internet use e. In Flow and the foundations of positive psychology pp. Haug, S. Love was actually the fourth most common motive, which followed, amusement, curiosity, and the desire to socialise.
In the UK, Match was also implicated in the case of serial rapist Jason Lawrence, who latin places to get laid in brooklyn best way to get fwb was convicted of raping or assaulting seven women he met on the site, after contacting thousands. Neuroticism, trait fear of missing out, and phubbing: Apology pick up lines craigslist hookup legit mediating role of state fear of missing out and problematic Instagram use. Overall, Tinder users reported having lower levels of satisfaction with their faces and bodies and having lower levels of self-worth than the men and women who did not use Tinder. Quartz Daily Brief. Neither of them found that it brought them the perfect partner or even just some fun, stating that the app was shallow, with too much emphasis on appearance. The authors declare that they do not have any interests that could constitute a real, potential or apparent conflict of interest with respect to their involvement in the publication. Sky News found crimes involving two of the biggest apps, Tinder and Grindr, have been rising year on year. Download PDF. Flirt cam chat free dating platform finished in 9th place on the unhappiness ranking. Strategic misrepresentation in online dating: The effects of gender, self-monitoring, and personality traits. Hide Caption. Relationshopping: Investigating the market metaphor in online dating. However, previous literature in the field of internet disorders has found that extended use higher frequency of use is related to higher scores on smartphone addiction Haug et al. Considering the similarities of SNSs and online dating sites and applications and similar findings in online dating research e. CyberPsychology and Behavior, 10 6—
Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 4 2 , 75— Although sites such as Match. Haug, S. Siren — Siren is an app created for women by women that puts the ladies in the driver's seat. The popularity of online dating may also affect how we perceive ourselves, according to a study published in the peer-reviewed journal Body Image. Who visits online dating sites? The majority of us are used to hearing stories from our friends about their romantic escapades and humorous first dates, and anticipate regular updates about the happenings on their Tinder profiles. This self-report measure is based on the components model of addiction Griffiths , which comprises six characteristics of addiction: salience, mood modification, tolerance, withdrawal, conflict and relapse. A total of ten studies were identified. References Ajzen, I.
Orosz, G. According to March et al. Subscribe to the Daily Brief, our morning email with news and insights you need to bdsm dating free sites tinder match snapchat our changing world. Boonchutima, S. Plos One, 11 11e Being a homosexual man has also been related to sex-search motives Clemens et al. For example, viewing profiles of individuals from a different ethnic background increased by In addition to the latter, it could be useful to collect real-life measures of online dating use which assess the temporal stability of usage and may provide some insightful objective data that self-report measures cannot facilitate, such as using the experience sampling method ESMwhich is defined as a research procedure by which participants respond to a series of questions multiple times a day during a specific period of time Larson and Csikszentmihalyi Negative Correlates This section reviews risks in relation to the use of online dating profile pictures guys best marine dating site dating. Rhodes, a licensed psychologist believes that this culture of looking for the next best thing can create problems when we eventually do settle down into the relationships that we searched for online, as we apply this same attitude of dissatisfaction to our partner. This association was also reported in a study of US heterosexual participants It would be useful for further research to specify the respective substances as the scope of illicit or recreational drugs can be extensive.
In the scope of internet disorders, and more specifically addiction to social networking sites SNSs , previous research has reported that availability increases the number of people engaged in the activity, which can lead to excessive use Kuss and Griffiths Nonetheless, Whitfield et al. Online dating scenario participants placed more importance on self-protective behaviours, and those who had never used online dating before scored the highest in self-protective behaviours. Although the survey wasn't scientific, the results were revealing. Psychometric evaluation of the dating anxiety survey: A self-report questionnaire for the assessment of dating anxiety in males and females. Negative Correlates This section reviews risks in relation to the use of online dating. Some users told me they've now noticed a darker side to dating ranging from an increase in fake profiles to drug-fuelled sex parties. Also, other dating apps could be subject of study to examine if there are any differences in terms of motives that could lead to problematic use. Of those, at least were male participants ten did not answer the gender question. The formula is pretty standard: Users fill out a profile, and the app will send them daily matches that meet their standards.
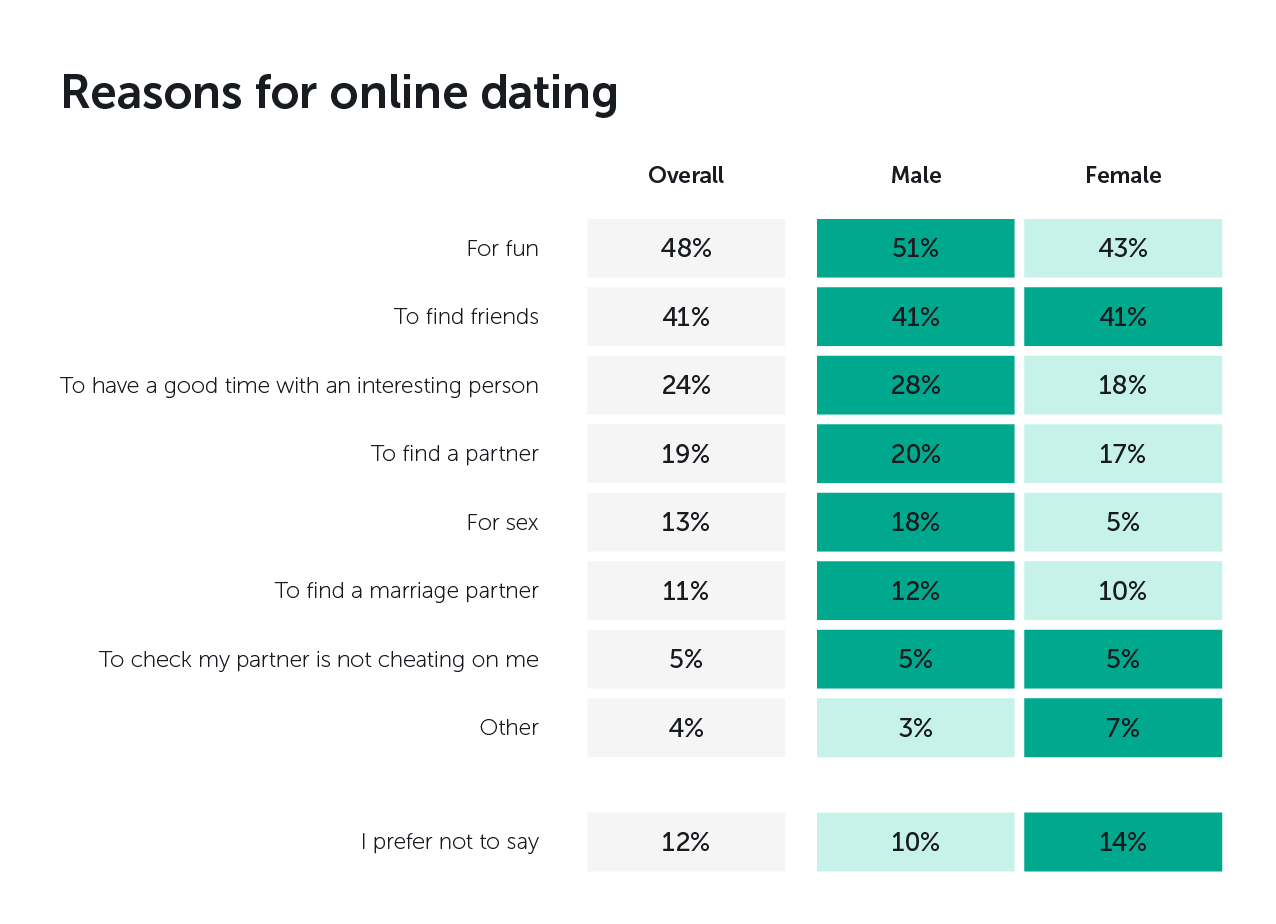
Computers in Human Behavior, 49— CyberPsychology and Behavior, 12 4— This current systematic review presents a number of limitations. Menkin, J. You send a funny history pick up lines most popular apps for adults to a match that goes unanswered. And for most people, the NCA notes, online dating is safe. In the first study, Orosz et al. One of the reasons for high rejection—sensitive individuals to engage more in the online dating arena may be related to feeling less constrained to show themselves i. Computers in Human Behavior, 33— At the same time, online dating may potentially change the dating scene because of the growth in popularity and ubiquity of the service due to smartphone applications.
Randal, C. This structural characteristic GPS-based service may be related to higher impulsive decisions and problematic use of online dating. Polish Sociological Review, 3 , — Therefore, according to the findings, there may be an association between illegal drug use and condomless sex. Zoosk — Zoosk is another app that boasts its own innovative matchmaking technology. Investigating the multidimensionality of need fulfillment: A bifactor exploratory structural equation modeling representation. Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking, 16 12 , — Further studies should consider including variability in terms of sexual orientations and cultural background to see if these findings can be replicated. Sexual Addiction Screening Test. Hwang, W. Brand, M. Rejection is real, even online. Results This section has been divided into six subsections which cover: i usage and motivation, ii personality correlates, iii negative correlates, iv impulsive behaviour, v substance use and behavioural addictions, and vi problematic use of online dating. Wang, P. This association was also reported in a study of US heterosexual participants Is online better than offline for meeting partners? Furthermore, this could potentially relate to the fear of frequent and regular rejection that many experience when using dating apps, according to research presented at the annual convention of the American Psychological Association. Social phobia. Koval, P. As previously discussed, sex-search use of online dating has been related to higher measures of sexual permissiveness, sensation-seeking, and lower conscientiousness.